Describe the Effects of Polygenic Inheritance Using Two Specific Examples
The more dominant alleles are inherited at each gene the more melanin is produced and the darker the skin color. Or hits with common diseases have conformed overwhelmingly to a standard pattern of many small polygenic effect.

Polygenic Inheritance Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary
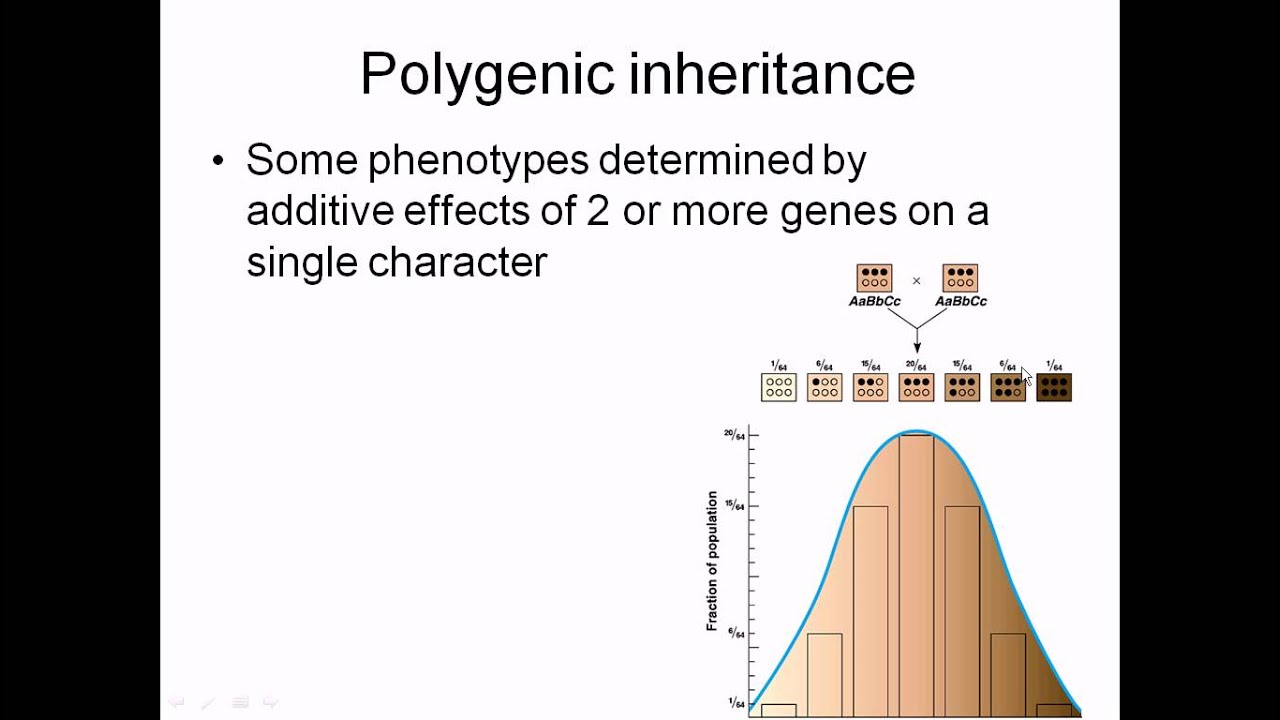
Polygenic inheritance This involves the inheritance and expression of a phenotype being determined by many genes at different loci with each gene exerting a small additive effect.
. 8 Total 20 marks 10. 1032 Explain that polygenic inheritance can contribute to continuous variation using two examples one of which must be human skin colour. ABO group in human is an example of codominance whereas flower colour of 4 O clock plant is an example of incomplete dominance.
In polygenic inheritance several sets of alleles may produce cumulative effect on the same character ie human height and colour of skin and eye. This inheritance pattern is sometimes called polygenic inheritance poly - many. Allele of each gene promotes pigment production or not other.
A Define the term gene linkage and outline an example of a cross between two linked genes. A polygenic characteristic is controlled by two genes each with two alleels How many different possible genotypes are there for this characteristic. This inheritance pattern is called polygenic inheritance poly many.
1032 Explain that polygenic inheritance can contribute to continuous variation using two examples one of which must be human skin colour Human Skin Colour The colour of human skin is determined by the amount of dark pigment melanin it contains. A classic example of this would be height. 2 a Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the fluid mosaic model of biological membranes.
Explain Mendels law of segregation and explain its mechanism based on molecular biology. Height in humans is very strongly genetically controlled but there are many many different genes that control height. Grain colour in wheat other valid example.
Height weight body shape eye color skin color and hair color of humans are controlled by the polygenic inheritance. More than one gene controlsaffects one characteristic. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers.
Instead of being measured discretely they are often represented as a range of continuous variation. And this is why people are not the exact height of their parents. Traits Phenotypes and Genotypes.
A Polygenic inheritance is an inheritance pattern controlled by three or more genes multiple genes and the graded phenotypes are due to the additive or cumulative effect of all the different genes of the trait. An example of human skin colour to understand the phenomenon of polygenic inheritance. 8 b Describe the inheritance of ABO blood groups including an example of the possible outcomes of a homozygous blood group A mother having a child with a blood group O father.
Albinism phenylketonuria autism schizophrenia sickle cell anemia and Marfan syndrome are examples of pleiotropy. For instance a recent study found over 400 genes linked to variation in height 1. No one gene is dominant or recessive to another.
Skin colour in humans is caused by a pigment called melanin. Fisher returned only once to the analysis of quantitative inheritance using the infinitesimal model and this was in. 3 Saved Complete the following paragraph to describe the inheritance of polygenic traits.
Some examples of polygenic traits are height skin color eye color and hair color. Allele of each gene promotes melanin production or not other valid example. Skin color is an example of a polygenic trait.
A polygenic trait is a characteristic sometimes we call them phenotypes that are affected by many many different genes. These genes are collectively called polygenes. Additive implies that the effects of the genes are cumulative ie.
Contrast incomplete dominance and incomplete penetrance and give examples. B Describe the effects of polygenic inheritance using two specific examples. Other traits are controlled by even.
Skin colour other valid example. Both pleiotropy and polygenic inheritance occur in all living organisms. Discuss the importance of melanin and UV radiation for skin coloration using specific examples.
Height and other similar features are controlled not just by one gene but rather by multiple often many genes that each make a small contribution to the overall outcome. 5 c Explain the process of transcription in eukaryotes. Contrast blending and the particulate concept of inheritance.
Because multiple genes are involved polygenic traits do not follow Mendels pattern of inheritance. Describe the effects of pleiotropy on phenotypic traits and provide examples of two. For example being expressed in a specific tissue or acting in a particular enzyme pathway.
For instance a recent study found over 400 genes linked to variation in height. When there are large numbers of genes involved it becomes hard to distinguish the effect of each individual gene and even harder to see that gene variants alleles are inherited. Since a single characteristic may be influenced by more than one gene it may exhibit continuous variation within a population.
Bell-shaped As you have learned many traits exist in humans that are controlled by a gene with either two allelic forms or where the gene exists in several allelic forms several There are still other traits such as skin color govemed byil genes each with their own sets of alleles and height. Reject more than 2 alleles can cause continuous variation many different possible phenotypes.

Comments
Post a Comment